Clinical Evidence
The efficacy of MyndMove™ therapy is supported by numerous clinical studies, including randomized controlled trials in both stroke and spinal cord injury populations.
MyndMove™ is the culmination of years of laboratory and clinical research by Dr. Milos R. Popovic, Toronto Rehab Chair in Spinal Cord Injury Research at the Toronto Rehab Institute – University Health Network, and professor at the Institute of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering at the University of Toronto.
Three randomized control studies, two looking at SCI and one looking at stroke patients, examined the effect of FES therapy using the MyndMove™ protocols. These studies found that patients who underwent 40 one-hour long sessions, 3-5 times per week over an 8-12 week period, demonstrated significant and lasting recovery of voluntary arm and hand movement. Patients participating in these studies represented those with some of the most severe deficits in motor function.
Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of MyndMove™ protocols as FES therapy to improve hand and arm function in:
- individuals with C3-C7 incomplete SCI
- individuals with severe hemiplegia due to stroke
Studies evaluated improved hand and arm function based on:
- Self-Care Functional Independence Measure (FIM) score
- Spinal Cord Independence Measure (SCIM) Self-Care Subscore
- Fugl-Meyer Assessment Upper Extremity (FMA-UE) of Motor Recovery after stroke score
Videos highlighting patients participating in this research have been prepared by UHN and the Rehabilitation Engineering Laboratory.
Stroke Rehabilitation
Studies have demonstrated that FES therapy using MyndMove™ protocols can lead to lasting recovery of upper extremity function in individuals who have experienced stroke, including:
- severe hemiplegia after acute stroke
- severe chronic hemiplegia due to stroke
Individuals experiencing severe upper extremity paralysis who were 2-7 weeks post-acute stroke took part in the study. 7,8 The patients that underwent one hour sessions of FES therapy with MyndMove™ 5 days a week for 12-16 weeks improved significantly more than patients undergoing conventional occupational therapy for the same timeframe in:
- Object manipulation, palmar grip torque, pinch grip pulling force (P<0.05)
- Barthel Index (P<0.05)
- Self-Care Functional Independence Measure (pictured) (P=0.005)
- Upper extremity Fugl-Meyer scores (P=0.003)
Self-Care Functional Independence Measure (SC-FIM)
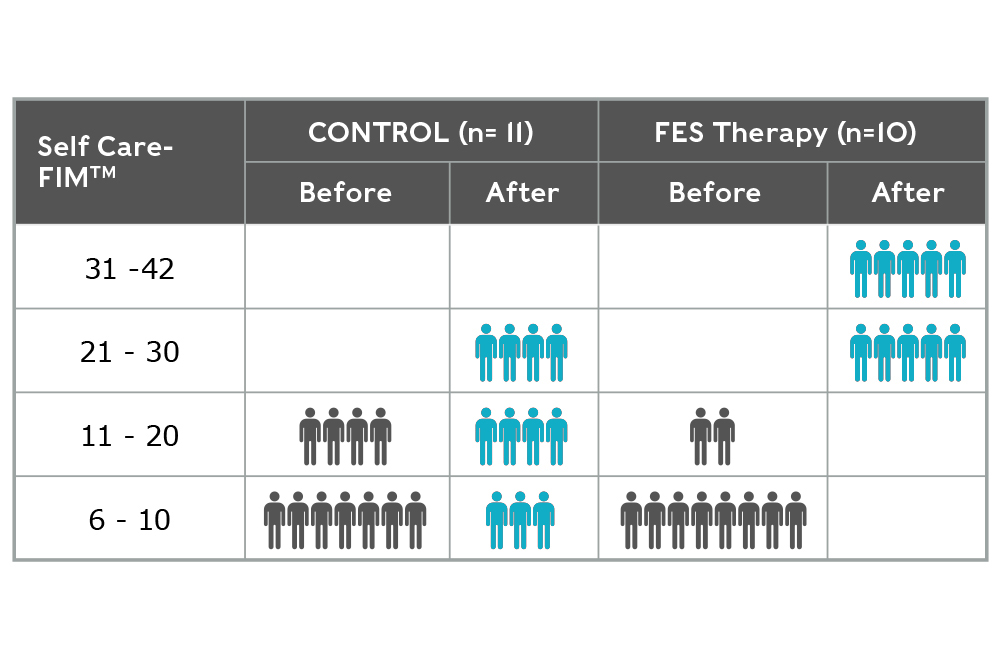
Self-Care Functional Independence Measure (FIM) measures an individual’s ability to feed, bathe, dress, groom, and toilet themselves after stroke. Minimum scores are 6, which indicates full dependence, maximum scores are 42 which indicates full independence.
SCI Rehabilitation
Studies have demonstrated that FES therapy using MyndMove™ protocols can lead to lasting recovery of upper extremity function in individuals with SCI, including:
- chronic incomplete SCI
- subacute incomplete SCI
- C3-C7 SCI
Individuals experiencing upper extremity paralysis due to SCI who underwent 40 hours of FES therapy with MyndMove™ + 40 hours of conventional occupational therapy (COT) over an 8 week period improved significantly more than patients who underwent 80 hours of COT during the 8 week period1,5. The patients were treated 5 days per week over the 8 week period. The difference in the mean change in SCIM self-care subscores from baseline to post treatment was statistically significant for the FES + COT group when compared to the COT only group (P< 0.0001).
Spinal Cord Independence Measure (SCIM) Self-Care Subscore
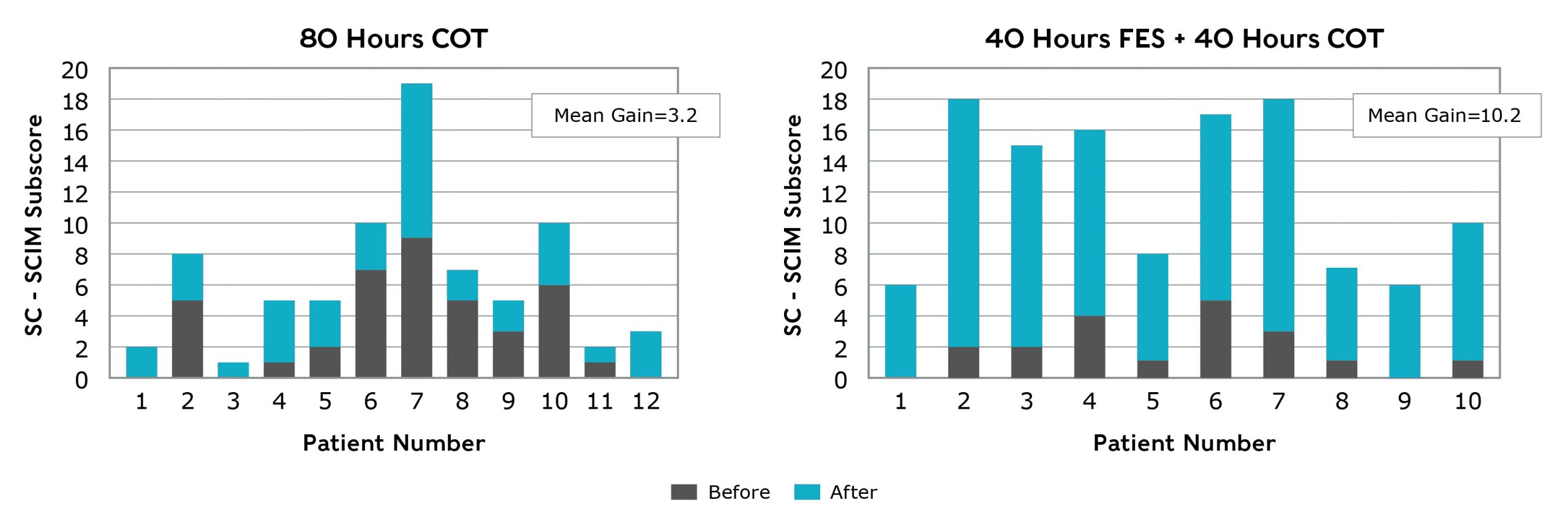
SCIM self-care subscore measures an individual’s ability to feed, bathe, dress, groom and toilet themselves. The minimum score is 0 (dependent) and the maximum score is 20 (independent).
In this study, FES therapy with MyndMove™ delivered by therapists effectively increased independence and thereby improved the quality of life of individuals with tetraplegia when compared with conventional occupational therapy alone.
Ongoing Studies: Active Multicenter Study
Restoration of Reaching and Grasping Function in individuals with Spinal Cord injury using MyndMove™ Neuromodulation Therapy
This study is designed as a multicenter, parallel group, two arm, single-blind, randomized controlled trial to compare the clinical outcomes of MyndMove™ therapy to intensive conventional therapy for individuals with C4-C7 traumatic incomplete SCI with upper extremity paresis. Treatments will commence in the outpatient setting. Study participants will be stratified by rehabilitation site and will be allocated in a 1:1 ratio to the following two treatment arms:
- MyndMove™ therapy: Participants will receive a minimum-maximum of 36-40 one-hour sessions of MyndMove™ therapy for up to 14 weeks.
- Intensive conventional therapy: Participants will receive upper-limb conventional therapy of equivalent frequency, intensity, and duration to MyndMove™ therapy (i.e. a minimum-maximum of 36-40 one-hour sessions of conventional therapy for up to 14 weeks)
For further details visit https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03439319
U.S. Department of Defense Clinical Trial Award in SCI: MyndTec is conducting this study through a grant from the U.S. Department of Defense.
Sponsor:
- MyndTec Inc.
Collaborators:
- U.S. Army Medical Research Acquisition Activity
- United States Department of Defense
- Programs for Assessment of Technology in Health Research Institute
- McMaster University
Studies Referenced
- Kapadia N, Shaghayegh B, Popovic MR. Influence of Different Rehabilitation Therapy Models on Patient Outcomes: Hand Function Therapy in Individuals with Incomplete SCI. The Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine. 2014:0:0-1.
- Kapadia N, Zivanovic V, Furlan J, Craven BC, McGillivray C, Popovic MR. Functional Electrical Stimulation Therapy for Grasping in Traumatic Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury: Randomized Control Trial. Artif Organs. 2011:35(3):212-216.
- Kapadia N, Zivanovic V, Popovic MR. Restoring Voluntary Grasping Function in Individuals with Incomplete Chronic Spinal Cord Injury: Pilot Study. Topics in Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation. 2013:19:4-279.
- Kawashima N, Popvic MR, Zivanovic V. Effect of Intensive FES Therapy on Upper-Limb Motor Recovery After Stroke. Physiotherapy Canada. 2013:65(1):20-28.
- Popovic MR, Kapadia N, Zivanovic V, Furlan J, Craven BC, McGillivray C. Functional Electrical Stimulation Therapy of Voluntary Grasping Versus only Conventional Rehabilitation for Patients with Subacute Incomplete Tetraplegia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair. 2011:25:5-433.
- Popovic MR, Thrasher T, Adams M, Takes V, Zivanovic V, Tonack M. Functional Electrical Therapy: Retraining Grasping in Spinal Cord Injury. Spinal Cord. 2006:44-143.
- Marquez-Chin C, Bagher S, Zivanovic V, Popovic MR. Functional electrical stimulation therapy for severe hemiplegia: Randomized control trial revisited. Canadian Journal of Occupational Therapy. 2017:84(2):87-97
- Trasher T, Zivanovic V, Mcllroy W, Popovic MR. Rehabilitation of Reaching and Grasping Function in Severe Hemiplegic Patients Using Functional Electrical Stimulation Therapy. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair. 2008:22:706-13.

